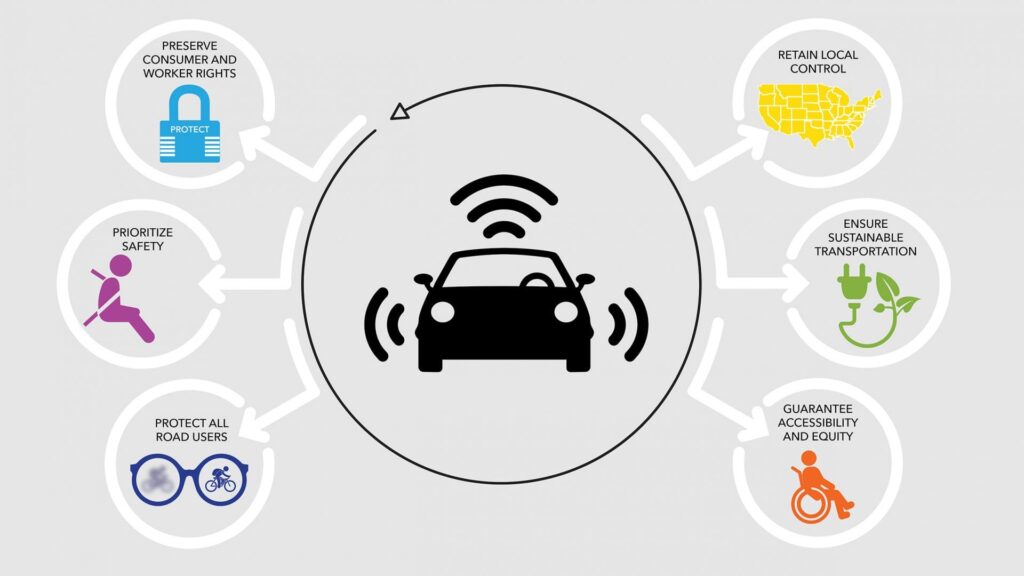
In the fast-paced world of autonomous vehicles, safety remains a top priority. As technology continues to advance and self-driving cars become more prevalent on our roads, it is essential to ensure reliable decision-making in these vehicles. With lives at stake, it is imperative that autonomous vehicles make sound judgments and prioritize the well-being of their passengers and those around them. In this article, we will explore the measures that are being taken to guarantee the safety of autonomous vehicles and the importance of reliable decision-making in this rapidly evolving industry.
Challenges in Decision-Making for Autonomous Vehicles
Limited environmental information
One major challenge in decision-making for autonomous vehicles is the limited environmental information available to them. While human drivers can rely on their senses to assess their surroundings and make decisions accordingly, autonomous vehicles rely on sensors, such as cameras, lidar, and radar, to gather information about their environment. However, these sensors have their limitations and may not always provide a complete and accurate picture of the vehicle’s surroundings. This can pose challenges in situations where the vehicle needs to make split-second decisions based on incomplete or unreliable data.
Real-time decision-making
Another challenge for autonomous vehicles is the need for real-time decision-making. Autonomous vehicles operate in dynamic environments where situations can change rapidly. They need to make decisions quickly and effectively to navigate through traffic, respond to obstacles, and ensure the safety of passengers and pedestrians. However, real-time decision-making requires processing large amounts of data within milliseconds and selecting the most appropriate course of action. This poses a significant challenge for autonomous vehicles, as the decision-making process needs to be both accurate and time-efficient.
Complex moral and ethical choices
One of the most complex challenges in decision-making for autonomous vehicles is the need to make moral and ethical choices. Autonomous vehicles may encounter situations where they have to decide between different courses of action that could potentially result in harm to different parties. For example, in a situation where a crash is unavoidable, the vehicle needs to decide whether to prioritize the safety of its passengers, other vehicles, or pedestrians. These decisions raise important ethical questions and require careful consideration to ensure that the vehicles prioritize safety and minimize harm in such situations.
Developing Reliable Decision-Making Frameworks
Machine learning algorithms
Developing reliable decision-making frameworks for autonomous vehicles involves the use of machine learning algorithms. Machine learning algorithms enable the vehicles to learn from data and make informed decisions based on patterns and past experiences. These algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data collected from sensors and other sources to identify potential risks, predict outcomes, and select the most appropriate actions. By continuously learning and adapting, machine learning algorithms can improve the decision-making capabilities of autonomous vehicles over time.
Deep neural networks
Deep neural networks are a key component of reliable decision-making frameworks for autonomous vehicles. These networks are designed to replicate the human brain’s structure and function, enabling the vehicles to process complex information and make intelligent decisions. Deep neural networks excel at recognizing patterns and extracting meaningful insights from large datasets, allowing autonomous vehicles to understand their environment and make informed decisions accordingly. By leveraging the power of deep neural networks, autonomous vehicles can enhance their decision-making capabilities and improve overall safety.
Reinforcement learning
Reinforcement learning is another technique used in the development of reliable decision-making frameworks for autonomous vehicles. This approach involves training the vehicles through trial and error, using rewards and penalties to guide their behavior. By repeatedly interacting with their environment and receiving feedback on their actions, autonomous vehicles can learn to make better decisions over time. Reinforcement learning allows the vehicles to adapt to changing conditions, respond to unexpected situations, and continually improve their decision-making abilities.
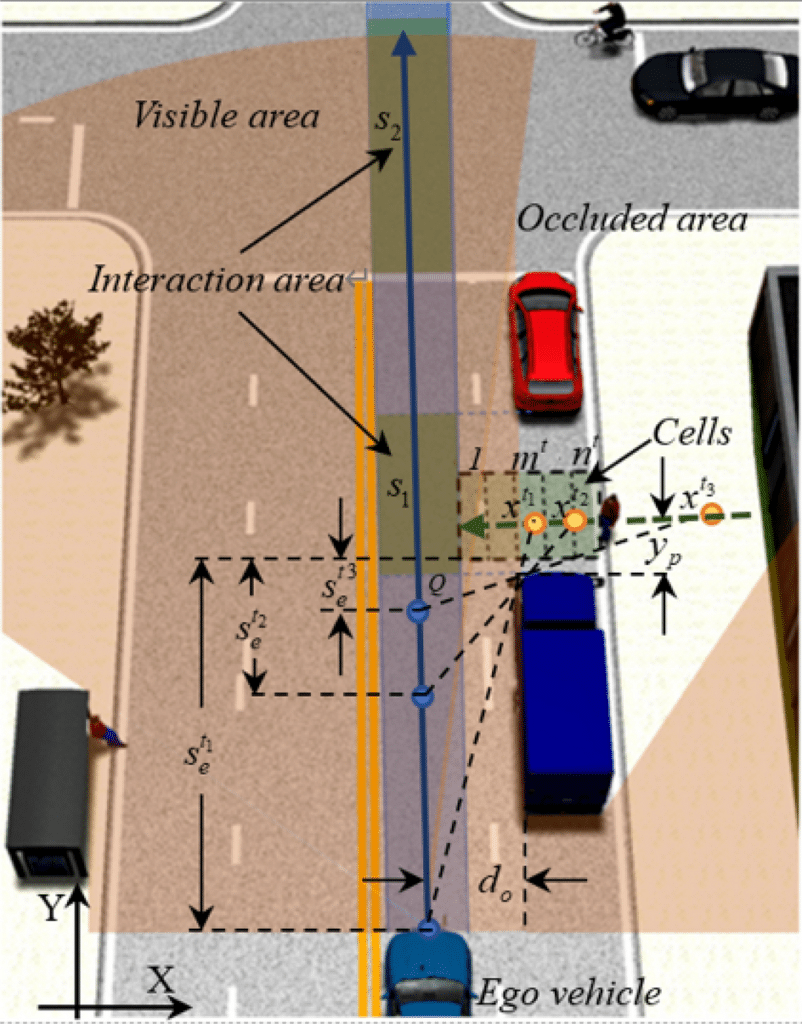
Safety Measures and Redundancy Systems
Collision avoidance systems
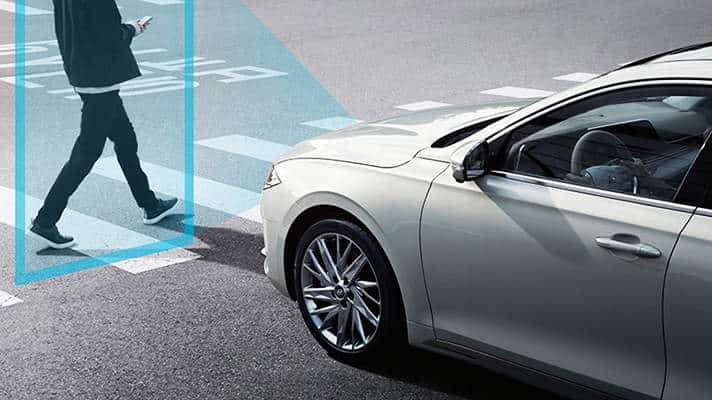
Safety measures such as collision avoidance systems play a crucial role in ensuring reliable decision-making in autonomous vehicles. These systems use a combination of sensors, algorithms, and actuators to detect and prevent potential collisions. By constantly monitoring the vehicle’s surroundings, collision avoidance systems can alert the vehicle to any imminent risks and take appropriate actions to avoid accidents. From emergency braking to evasive maneuvers, these safety measures help enhance the decision-making capabilities of autonomous vehicles and minimize the likelihood of accidents.
Sensor redundancy
To enhance the reliability of decision-making, autonomous vehicles often employ sensor redundancy. This means that multiple sensors of the same type or different types are used to gather environmental information. By relying on redundant sensors, the vehicles can cross-verify the data they receive and detect any inconsistencies or failures. Sensor redundancy helps reduce the risk of relying on a single point of failure and provides a more robust and accurate picture of the vehicle’s surroundings. This enables the vehicles to make more informed and reliable decisions, even in challenging or uncertain situations.
Backup control mechanisms
Backup control mechanisms are another important safety measure to ensure reliable decision-making in autonomous vehicles. These mechanisms serve as a failsafe in case of a failure or error in the primary control system. Backup control mechanisms can include redundant computing systems, backup power supplies, or even human intervention capabilities. By having reliable backup systems in place, autonomous vehicles can quickly switch to alternative control mechanisms if needed, ensuring the safety of the vehicle and its passengers. These redundancies provide an additional layer of protection and help maintain the reliability of decision-making in autonomous vehicles.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Liability and responsibility
Legal and ethical considerations play a significant role in shaping decision-making frameworks for autonomous vehicles. As autonomous vehicles become more prevalent on the roads, questions arise regarding liability in the event of accidents or incidents. Determining who is responsible for any damages or injuries caused by autonomous vehicles is a complex issue that requires clear legal frameworks. These frameworks need to address questions of accountability, insurance coverage, and liability allocation to protect the rights and safety of individuals involved.
Regulatory frameworks
Regulatory frameworks are essential in ensuring the safe and responsible deployment of autonomous vehicles. Governments and regulatory bodies need to establish standards and guidelines that govern the development, testing, and operation of autonomous vehicles. These frameworks should outline the minimum safety requirements, data privacy regulations, and ethical guidelines that autonomous vehicle manufacturers and operators must adhere to. By establishing clear regulations, governments can ensure that autonomous vehicles operate in a manner that prioritizes safety, fairness, and accountability.
Ethical programming choices
The ethical programming choices made in the development of autonomous vehicles’ decision-making systems are crucial. These choices involve determining how the vehicles should prioritize different values and make moral and ethical decisions. For example, should an autonomous vehicle prioritize the safety of its passengers over other road users? How should the vehicle respond in situations where harm is unavoidable? These ethical programming choices need to be carefully considered and based on societal norms, legal requirements, and public input. Incorporating ethical considerations into decision-making systems is crucial to ensure that autonomous vehicles act in ways that align with human values and minimize harm.
Testing and Validation Processes
Simulated testing
Simulated testing is an essential part of developing reliable decision-making frameworks for autonomous vehicles. Simulations allow developers to create virtual environments that replicate real-world scenarios and test the behavior of autonomous vehicles in a controlled setting. Simulated testing enables the vehicles to be exposed to a wide range of challenging situations, helping developers identify and rectify any weaknesses or limitations in their decision-making capabilities. By simulating different scenarios, autonomous vehicle developers can refine their algorithms, validate their performance, and enhance the overall reliability of their decision-making systems.
Closed-course testing
Closed-course testing involves putting autonomous vehicles through rigorous testing on controlled tracks or closed circuits. This type of testing allows developers to assess the performance of their decision-making systems in real-world-like conditions while minimizing potential risks to the public. Closed-course testing often involves simulating various road scenarios, such as intersections, traffic congestion, and dynamic obstacles, to evaluate how the vehicles respond and make decisions. By conducting closed-course testing, autonomous vehicle developers can fine-tune their decision-making systems, optimize their performance, and ensure a high level of safety before transitioning to real-world testing.
Real-world testing
Real-world testing is a critical step in the development of autonomous vehicles’ decision-making frameworks. This involves deploying the vehicles on public roads under controlled conditions to gather data and assess their performance in real-world scenarios. Real-world testing allows developers to validate their decision-making systems in complex and dynamic environments, where they interact with other vehicles, pedestrians, and various road conditions. Gathering data from real-world testing helps identify potential weaknesses, challenges, and areas for improvement in the decision-making capabilities of autonomous vehicles. It provides valuable insights that can be used to enhance safety and overall reliability.
Human-Machine Interaction and Safety
Driver monitoring systems
Human-Machine Interaction (HMI) plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety of autonomous vehicles. Driver monitoring systems are an important component of HMI, as they enable the vehicle to monitor the driver’s attention and readiness to take over control if necessary. These systems use cameras and other sensors to track the driver’s eye movements, facial expressions, and other behavioral cues to assess their level of alertness. By continuously monitoring the driver’s state, the vehicle can detect signs of drowsiness, distraction, or other factors that may impact their ability to intervene in critical situations. Driver monitoring systems enhance safety by ensuring that the driver remains engaged and ready to take over control when needed.
Handover protocols
Handover protocols are another important aspect of HMI in autonomous vehicles. In situations where the autonomous vehicle is no longer able to handle a particular scenario or encounters an issue, it needs to be able to communicate and transfer control to the human driver effectively. Handover protocols define the procedures and communication channels for such transitions, ensuring a seamless transfer of control and minimizing any confusion or delay. Well-defined handover protocols help enhance safety by ensuring that the driver can promptly respond when the vehicle requires human intervention, ultimately improving the reliability of decision-making in autonomous vehicles.
Driver training and awareness
Driver training and awareness are vital in ensuring the safe integration of autonomous vehicles on the roads. Although the vehicles are designed to be highly autonomous, human drivers still play a crucial role in monitoring the vehicle’s actions and taking over control if necessary. Proper training and education for human drivers are essential to ensure that they understand the capabilities and limitations of autonomous vehicles, as well as their own responsibilities. By promoting driver awareness, providing comprehensive training programs, and fostering a culture of safety, the industry can further enhance the reliability of decision-making in autonomous vehicles and promote safe interactions between humans and machines.
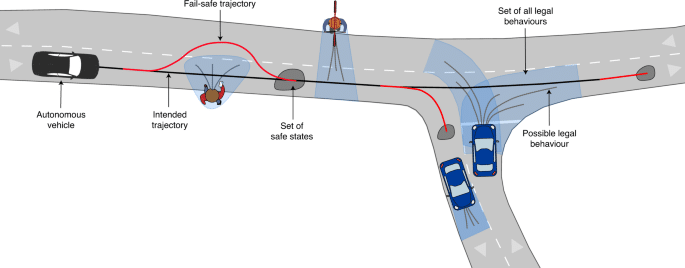
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
Protection against cyber threats
Data security is a paramount concern when it comes to autonomous vehicles. As these vehicles become increasingly connected and rely on data to make decisions, they also become potential targets for cyber threats. Unauthorized access to or tampering with the vehicle’s data can have severe consequences, compromising the safety and reliability of its decision-making systems. Protecting against cyber threats requires robust security measures, such as encryption, authentication protocols, and intrusion detection systems. By implementing strong security measures, autonomous vehicles can ensure the integrity and confidentiality of their data, enhancing the reliability of their decision-making processes.
Privacy of user data
Autonomous vehicles collect large amounts of data about their users, including their locations, preferences, and behaviors. Ensuring the privacy of user data is essential to maintain user trust and comply with legal and ethical requirements. Autonomous vehicle manufacturers and operators need to implement strict privacy policies and protocols to safeguard user data. These policies should outline transparent data collection and usage practices, provide users with control over their data, and protect against unauthorized access or disclosure. By prioritizing privacy, autonomous vehicles can foster trust among users and ensure the reliability of their decision-making systems.
Data encryption
Data encryption is a critical security measure to protect the integrity and confidentiality of autonomous vehicle data. Encryption transforms data into a coded form that can only be deciphered with the appropriate decryption key. By encrypting the data collected by autonomous vehicles, even if it is intercepted or accessed by unauthorized parties, it remains unintelligible and unusable. Strong encryption algorithms and practices need to be employed to ensure the effectiveness of data encryption. By implementing robust data encryption measures, autonomous vehicles can enhance the security of their decision-making systems and protect the privacy of user data.
Continuous Improvement and Updates
Software updates
Continuous improvement and updates are essential to ensure the reliability of decision-making in autonomous vehicles. Software updates enable developers to address vulnerabilities, enhance performance, and incorporate new features and capabilities. These updates can include bug fixes, security patches, and advancements in decision-making algorithms. Promoting regular software updates and providing mechanisms for over-the-air updates ensures that autonomous vehicles remain up-to-date and benefit from the latest advancements in decision-making technology. By continuously improving and updating their software, autonomous vehicles can adapt to evolving challenges, enhance their decision-making capabilities, and maximize safety and reliability.
Machine learning models refinement
Refining machine learning models is an integral part of continuous improvement in autonomous vehicle decision-making frameworks. Machine learning models used by autonomous vehicles learn from data and continuously adapt their behavior based on feedback. Regularly refining these models helps improve their accuracy, robustness, and ability to make informed decisions. By analyzing data collected from real-world testing and user feedback, developers can identify areas where the models may be lacking and make the necessary adjustments. By focusing on the continual refinement of machine learning models, autonomous vehicles can enhance their decision-making capabilities and improve overall safety.
Sharing data for collective learning
Sharing data for collective learning is a collaborative approach to improving decision-making in autonomous vehicles. By sharing anonymized and aggregated data with other manufacturers and developers, valuable insights can be gained, and common challenges can be addressed more effectively. Shared data can help train and validate decision-making models, identify emerging trends, and refine algorithms. Collaborative research initiatives and data sharing agreements facilitate the sharing of data and ensure that new knowledge and advancements benefit the entire industry. By embracing collective learning, autonomous vehicle developers can accelerate the improvement of decision-making capabilities, fostering innovation and safety advancements.

Industry Collaboration and Standards
Collaborative research initiatives
Collaborative research initiatives are an important driver of progress in autonomous vehicle decision-making. By bringing together researchers, industry stakeholders, and academic institutions, collaborative research initiatives facilitate the exchange of knowledge, ideas, and resources. These initiatives promote interdisciplinary collaboration, enabling experts from different fields to contribute their expertise to enhance decision-making capabilities. Through collaborative research, issues and challenges in autonomous vehicle decision-making can be collectively tackled, paving the way for innovative solutions and industry-wide advancements.
Technical standards for safety
Establishing technical standards for safety is vital to ensure the reliability of decision-making in autonomous vehicles. Technical standards provide guidelines and benchmarks that autonomous vehicle manufacturers and developers can adhere to, ensuring a common level of safety across the industry. These standards address various aspects of decision-making, such as sensor performance, algorithmic robustness, and behavioral guidelines. By following standardized safety requirements, autonomous vehicles can achieve a high level of reliability and interoperability, enhancing overall safety and public trust.
Data sharing agreements
Data sharing agreements facilitate the exchange of data among autonomous vehicle manufacturers and operators. These agreements outline the terms and conditions under which data can be shared, ensuring that the privacy and security of the data are protected. Data sharing agreements can foster collaboration, allowing manufacturers to learn from each other’s experiences, validate their decision-making systems, and collectively improve safety. By establishing transparent and cooperative data sharing practices, the industry can benefit from shared insights and promote the reliability of decision-making in autonomous vehicles on a broader scale.
Balancing Safety and Efficiency
Optimizing decision-making speed
Finding the right balance between safety and efficiency is a core challenge in decision-making for autonomous vehicles. While safety is paramount, ensuring that the vehicles make decisions at a speed that allows smooth traffic flow and minimizes disruptions is also crucial. Optimization techniques, such as real-time path planning algorithms, can help strike this balance. These algorithms dynamically evaluate multiple factors, such as traffic conditions, pedestrians’ movements, and surrounding vehicle behavior, to compute the most efficient and safest paths for the vehicles. By optimizing decision-making speed, autonomous vehicles can navigate complex environments while maintaining high levels of safety and efficiency.
Prioritizing safety over convenience
To ensure reliable decision-making, autonomous vehicles must prioritize safety over convenience. This means making decisions that prioritize the well-being of passengers, other road users, and pedestrians, even if it may result in inconvenience or delays. For example, autonomous vehicles may need to slow down or yield to pedestrians, maintain safe distances from other vehicles, or avoid risky maneuvers. By prioritizing safety, autonomous vehicles can build trust among the public, reduce the likelihood of accidents, and ultimately contribute to a safer and more sustainable transportation system.
Adaptive risk assessments
Adaptive risk assessments are crucial for balancing safety and efficiency in autonomous vehicle decision-making. These assessments involve continuously evaluating the risks associated with different courses of action and adapting the vehicles’ behavior accordingly. For example, in congested traffic, the vehicles may need to adopt more cautious driving behavior to minimize the risk of collisions. Conversely, on open highways, they can adopt more efficient and higher-speed driving modes. By dynamically assessing risks and adapting their decision-making, autonomous vehicles can navigate different situations while maintaining an optimal balance between safety and efficiency.
Ensuring the reliable decision-making of autonomous vehicles is a complex endeavor that requires addressing various challenges, developing robust frameworks, and striking the right balance between safety and efficiency. Limited environmental information, real-time decision-making, and complex moral and ethical choices are just some of the challenges that need to be tackled. Developing reliable decision-making frameworks involves leveraging machine learning algorithms, deep neural networks, and reinforcement learning techniques. Safety measures and redundancy systems, as well as legal and ethical considerations, play a critical role in ensuring reliable decision-making. Testing and validation processes, human-machine interaction, data security and privacy, continuous improvement, industry collaboration, and standards all contribute to enhancing the reliability of decision-making in autonomous vehicles. Striking the right balance between safety and efficiency requires optimizing decision-making speed, prioritizing safety over convenience, and conducting adaptive risk assessments. By addressing these aspects comprehensively and collaboratively, the industry can pave the way for widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles and a future of safer and more efficient transportation.