In the exciting world of artificial intelligence, a groundbreaking technology has emerged: Generative Adversarial Networks, or GANs for short. These machines possess a remarkable ability to generate new and unique content, blurring the line between what is real and what is artificial. With GANs, the possibilities are endless, from creating lifelike images and videos to composing original music and writing compelling stories. In this article, we will explore the rise of GANs, their incredible potential, and how they are revolutionizing the field of AI. Get ready to be amazed by the machines with imagination!
Understanding Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
What are Generative Adversarial Networks?
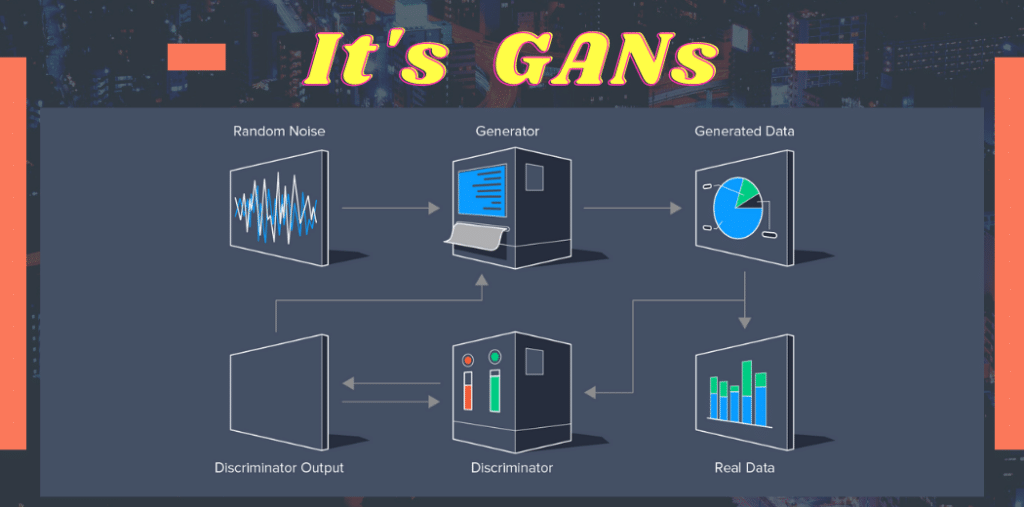
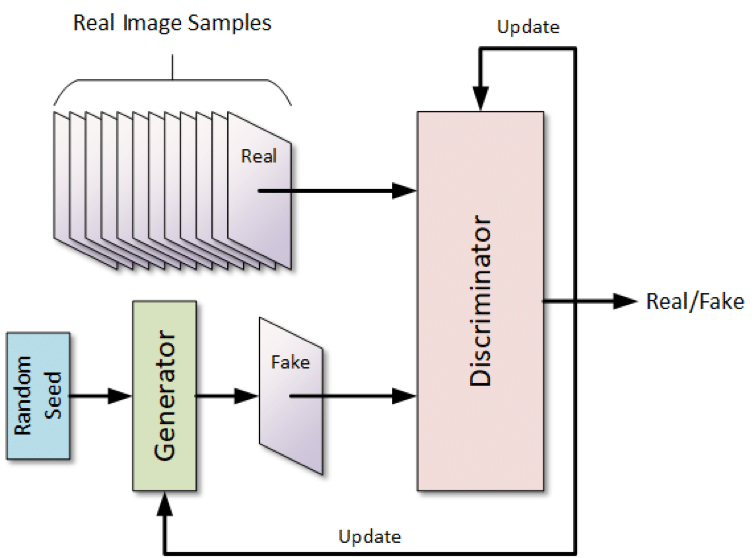
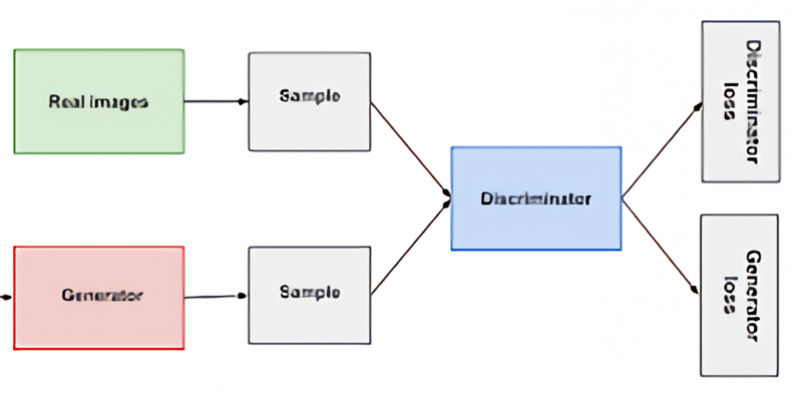
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are a type of machine learning model that consist of two neural networks: a generator and a discriminator. The generator network learns to generate new data instances that resemble a given training dataset, while the discriminator network aims to differentiate between real and generated data instances. GANs have gained significant attention in recent years due to their ability to create realistic and high-quality synthetic data.
How do GANs work?
The key idea behind GANs is to train the generator and discriminator networks simultaneously in a competitive manner. The generator takes random noise as input and generates synthetic data samples, which are then evaluated by the discriminator. The discriminator’s role is to classify the data as either real or fake (generated). Through this adversarial process, the generator gradually improves its ability to generate data that the discriminator has difficulty distinguishing from real data.
The key components of GANs
GANs consist of several key components that enable their functionality. First, the generator network is responsible for producing synthetic data based on random noise as input. The discriminator network, on the other hand, learns to distinguish between real and generated data samples. The loss function plays a crucial role in GANs, as it guides the training process by measuring the difference between the discriminator’s predictions and the true labels. Additionally, the training process often involves techniques such as minibatch discrimination and batch normalization to enhance stability and performance.
The Evolution of GANs
Early developments
The concept of GANs was introduced in 2014 by Ian Goodfellow and his colleagues, representing a significant milestone in the field of deep learning. Early versions of GANs faced challenges such as training instability and mode collapse, where the generator produces a limited variety of output samples. However, researchers quickly made improvements and developed techniques to address these issues, leading to the increased adoption and popularity of GANs across various domains.
Progress and advancements
Since their introduction, GANs have evolved tremendously, thanks to ongoing research and advancements. Researchers have developed different variations of GANs, such as conditional GANs, which allow for the generation of specific data samples based on additional input information. Progressive GANs have also emerged, enabling the generation of high-resolution images by gradually increasing the complexity of the generator and discriminator. Furthermore, techniques like self-attention mechanisms and style-based GANs have improved the quality and diversity of the generated output.
Current state of GANs
Currently, GANs are witnessing widespread adoption in various fields, including computer vision, natural language processing, and creative industries. Researchers continue to explore new architectures, loss functions, and training strategies to overcome limitations and push the boundaries of what GANs can achieve. With increasing computational power and data availability, GANs are poised to continue their trajectory of innovation and impact in the coming years.
Applications of Generative Adversarial Networks
Image synthesis and manipulation
GANs have revolutionized image synthesis and manipulation. They have been used to create realistic images that resemble specific styles, allowing artists and designers to generate novel and visually appealing content. GANs have also enabled image-to-image translation, where an input image is transformed into a different style or domain. This has applications in areas such as photo enhancement, style transfer, and virtual try-on, enhancing creativity and expanding the possibilities in digital art and design.
Text generation and translation
GANs have been successfully applied to text generation tasks, including the generation of realistic and coherent paragraphs, poems, and stories. By training GANs on vast amounts of textual data, models can learn to capture the underlying structure and style of the training corpus, enabling the generation of new text that closely resembles human-written content. GANs have also been utilized for text translation, facilitating the creation of multilingual communication tools and aiding in language understanding across different cultures.
Video generation and editing
GANs have recently been extended to the domain of video generation and editing. By applying the principles of GANs to sequential data, researchers have developed models capable of generating realistic videos and manipulating existing videos. This has implications in video production, special effects, and virtual reality experiences, where GANs can be used to create immersive and dynamic content. Video synthesis and editing using GANs offer new possibilities for filmmakers, game developers, and content creators to push the boundaries of visual storytelling.
Implications and Ethical Considerations
Potential societal impact
The advancements in GAN technology raise important considerations regarding its potential societal impact. GANs have the power to generate highly realistic and persuasive fake content, including images, videos, and text. While this can be used for creativity and entertainment purposes, it also raises concerns about the spread of disinformation, forgery, and malicious use. It is crucial to address these challenges and strike a balance between the benefits and risks associated with GANs.
Ethical concerns and challenges
As GANs become more sophisticated, ethical concerns regarding their usage become increasingly significant. The generation of deepfake content using GANs raises questions about privacy, consent, and misinformation. It is important to establish guidelines and regulations for the responsible use of GAN technology to ensure that individuals are not harmed or deceived by manipulated content. Transparency, accountability, and user awareness are essential in mitigating ethical challenges associated with GANs.
Mitigating risks and responsible use
To mitigate the risks associated with GANs, it is crucial to invest in research and development that focuses on identifying and detecting synthetic content. Improved detection methods can help differentiate between real and generated data, enhancing trust and reliability in the digital era. Additionally, promoting responsible use of GANs through awareness campaigns, education, and ethical guidelines can guide individuals and organizations in making informed decisions regarding the creation and dissemination of generated content.
Challenges and Limitations of GANs
Training instability and mode collapse
One of the major challenges in training GANs is instability, where the generator and discriminator networks struggle to find a balance during the adversarial training process. This can lead to poor convergence, where the generator fails to generate diverse and realistic data samples. Mode collapse is another limitation, where the generator only produces a limited variety of output. Researchers are actively working to develop novel training techniques and regularization methods to overcome these issues and improve the stability and diversity of GAN-generated output.
Data limitations and biases
The quality and quantity of training data play a crucial role in the success of GANs. Insufficient or biased training data can lead to poor performance and biased generation. Data limitations pose challenges in domains where obtaining large and diverse datasets is difficult, limiting the applicability of GANs in certain fields. Furthermore, the biases present in the training data can propagate into the generated output, potentially reinforcing societal biases and inequalities. Researchers and practitioners must address these data limitations and biases to ensure fairness and inclusivity in GAN applications.
Interpretability and explainability
Despite their impressive capabilities, GANs often lack interpretability and explainability. The black-box nature of GAN models makes it challenging to understand how they generate specific outputs and make decisions. Interpreting GAN-generated content can be difficult, especially in applications where accountability and transparency are crucial, such as healthcare and legal domains. Efforts are underway to develop methods for interpreting and explaining GAN-generated output, enabling better understanding and trust in their applications.
The Future of Generative Adversarial Networks
Integration with other AI technologies
The future of GANs lies in their integration with other AI technologies, such as reinforcement learning and natural language processing. Combining GANs with reinforcement learning can enable the generation of interactive and dynamic content, where the generated output is influenced by user feedback and preferences. Integration with natural language processing can allow for more sophisticated text generation and translation, producing highly coherent and context-aware content. Such advancements hold promise in various domains, including virtual assistants, interactive storytelling, and personalized content generation.
Enhancing creative processes
GANs have already demonstrated their potential in enhancing creative processes, such as art and design. As GANs continue to evolve, they are expected to contribute significantly to the field of creative arts by enabling artists and designers to explore new possibilities, express themselves in innovative ways, and push the boundaries of imagination. GANs can be used to assist in brainstorming, generate design variations, and inspire new artistic styles. The integration of human creativity and machine-generated content can lead to the emergence of novel artistic expressions and unique collaborative experiences.
Potential advancements and breakthroughs
The future of GANs holds great promise for advancements and breakthroughs in various fields. The continuous improvement of GAN architectures, training algorithms, and data handling techniques will likely lead to even more realistic and diverse synthetic content. From generating highly realistic and interactive virtual environments to aiding in drug discovery and molecular design, GANs have the potential to revolutionize industries and reshape our understanding of AI and machine learning capabilities. The exploration and utilization of GANs in new and unexplored domains are expected to unlock exciting possibilities in the years to come.
GANs in Industry and Research
Use cases in various industries
GANs have found applications in numerous industries, revolutionizing processes and creating new opportunities. In the fashion industry, GANs have been used for virtual clothes try-on, allowing customers to visualize how clothing items would look on them without physically trying them on. In the automotive industry, GANs have facilitated the synthesis of realistic 3D objects and textures for virtual prototyping and design. The applications of GANs extend to finance, robotics, entertainment, and many other sectors, showcasing the versatility and impact of this technology.
Impact on artistic and design fields
GANs have had a profound impact on artistic and design fields, empowering artists and designers with new tools and capabilities. Artists can leverage GANs to generate unique and inspiring visual content, explore various artistic styles, and enhance their creative process. GANs have also facilitated the design of new products, logos, and graphics, enabling designers to iterate and experiment efficiently. The integration of GANs in the creative workflow has opened doors to novel artistic expressions and collaborations between humans and machines.
Research and academic contributions
In the field of research and academia, GANs have made significant contributions across various domains. GANs have been employed in medical image analysis, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases by generating synthetic images for training and evaluation. Researchers have also utilized GANs for data augmentation, enhancing the diversity and size of training datasets in machine learning tasks. GANs have furthered our understanding of deep learning and adversarial training techniques, paving the way for future advancements and breakthroughs in the field of AI.
The Role of GANs in Art and Entertainment
Generating art and music
GANs have revolutionized the creation of art and music, offering new avenues for artistic expression and exploration. Artists can train GAN models on massive datasets of artworks or musical compositions, enabling the generation of entirely new pieces inspired by the learned styles. GANs can provide artists with a continuous stream of ideas and variations, encouraging creative discovery and innovation. Additionally, GANs can be used to generate personalized soundtracks, adapting music to specific moods or preferences, enhancing the entertainment experience for users.
Virtual reality experiences
In the realm of virtual reality (VR), GANs have the potential to shape immersive experiences. GANs can generate realistic and interactive virtual environments, enhancing the sense of presence and realism in VR applications. By training GANs on real-world data, developers can create virtual worlds that closely resemble their real-life counterparts. GANs can also be used to generate dynamic and responsive virtual characters, enabling more engaging and interactive interactions within virtual environments.
Collaboration between humans and machines
GANs have opened up new possibilities for collaboration between humans and machines in the field of art and entertainment. Artists and designers can use GANs as creative tools, providing them with new sources of inspiration and assisting in the creative process. GANs can generate initial design ideas, iterate on existing artwork, and even collaborate directly with artists to produce unique and innovative creations. This collaborative approach allows for the blending of human creativity and machine intelligence, fostering a new era of co-creation and exploration in the artistic and entertainment domains.
GANs and the Healthcare Sector
Medical image analysis and augmentation
GANs have shown immense potential in the healthcare sector, particularly in medical image analysis and augmentation. By training GANs on large datasets of medical images, models can learn to generate synthetic images that resemble real patient data. This has applications in data augmentation, where GANs can create additional training samples, improving the robustness and generalization of medical image analysis models. GANs can also aid in generating enhanced or denoised medical images, facilitating more accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Drug discovery and molecular design
GANs have the ability to accelerate drug discovery and molecular design processes. By training GANs on chemical compound data, models can learn to generate novel molecules with desirable properties. This has the potential to revolutionize the drug development pipeline, enabling the rapid exploration of vast chemical space and the identification of promising candidates for further testing. GANs can also assist in predicting and optimizing the properties of chemical compounds, leading to the discovery of more effective and safer drugs.
Improving patient outcomes
Through their various applications in healthcare, GANs have the potential to improve patient outcomes. By generating synthetic medical data, GANs can aid in creating personalized treatment plans and guiding surgical interventions. GAN-generated medical images can be used for training and evaluating AI models, enhancing their accuracy and performance. By leveraging the power of GANs, healthcare professionals can access a broader range of data and insights, leading to improved diagnoses, better treatment decisions, and ultimately, improved patient care.
The Importance of Data Quality and Bias
Ensuring diverse and representative datasets
High-quality datasets are vital for the success and reliability of GANs. Ensuring that training datasets are diverse and representative of the real-world population is crucial in generating unbiased and realistic synthetic data. Collecting and curating diverse datasets, considering factors such as age, gender, ethnicity, and socioeconomic background, helps mitigate biases and promotes fairness in GAN-generated content. The inclusion of diverse datasets enriches the training process and enables the generation of more inclusive and representative synthetic data.
Identifying and addressing bias
GANs are susceptible to biases present in the training data, and special attention should be given to identifying and addressing these biases. Biased training data can lead to the generation of discriminatory or misleading content, perpetuating stereotypes and inequalities. Researchers and practitioners must actively work towards identifying and mitigating biases in GAN-generated output. The development of bias detection mechanisms and the adoption of fair training practices are essential steps in addressing bias and ensuring ethical and unbiased use of GANs.
Responsible data collection and usage
Responsible data collection and usage are fundamental in the context of GANs. Privacy considerations should be taken into account when collecting and handling training data to protect individuals’ personal information. Organizations and researchers should follow ethical guidelines and legal regulations to ensure the responsible use of data in GAN applications. Transparency in data collection, data handling practices, and the GAN training process fosters trust and accountability, enabling the ethical use of GAN-generated content and reducing potential risks and harms.
In conclusion, the rise of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) has brought forth remarkable advancements in machine learning and artificial intelligence. GANs have shown immense potential in diverse domains such as image synthesis and manipulation, text generation and translation, and video generation and editing. However, the adoption of GANs also raises implications and ethical considerations, including potential societal impact, ethical concerns, and challenges. It is imperative to address the challenges and limitations of GANs, such as training stability, data limitations, and interpretability. The future of GANs holds exciting possibilities, including integration with other AI technologies, enhancing creative processes, and potential advancements and breakthroughs. GANs are making significant strides in industry and research, impacting various sectors and contributing to academic advancements. Furthermore, GANs play a vital role in the art and entertainment industry, generating art and music, enabling virtual reality experiences, and fostering collaboration between humans and machines. GANs also hold immense potential in the healthcare sector, facilitating medical image analysis, aiding in drug discovery, and improving patient outcomes. Finally, the importance of data quality and bias in GANs cannot be overstated, emphasizing the need for diverse and representative datasets and responsible data collection and usage. With responsible development and usage, GANs can continue to enrich our lives and drive innovation in the realm of artificial intelligence and beyond.